Rising Salmonella Cases Raise Concerns Across the UK
Recent health reports have highlighted a concerning increase in salmonella infections across the United Kingdom. The rise is attributed to two rare strains of the bacteria—Salmonella Blockley (S. Blockley) and Salmonella Strathcona. These strains, typically more common in regions like East Asia and the US, have been linked to several outbreaks in the UK, raising alarms among health officials.
In 2024 alone, over 100 individuals were affected by these infections, with at least 14 people requiring hospitalization. The cases were not limited to a specific region but were reported nationwide, according to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA). This widespread distribution has made it challenging for authorities to trace the exact source of contamination.
Understanding the Bacteria
Salmonella is a group of bacteria that commonly infects the gastrointestinal tract of animals. It can be found in various food sources, including meat, eggs, and poultry. While most cases result in temporary illness characterized by diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps, severe infections can lead to life-threatening complications.
The incubation period for salmonella ranges from 12 to 72 hours after ingestion. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as children and the elderly, are particularly vulnerable to severe illness. In some cases, dehydration caused by the infection may necessitate hospital care.
Outbreaks Linked to Tomatoes
According to the 2024 UKHSA data, there were 81 confirmed cases of S. Blockley, all linked to tomatoes. At least 14 of these individuals required hospitalization. Additionally, a separate outbreak involving Salmonella Strathcona affected 24 people, with tomatoes also suspected as the source.
However, the origin of the contaminated tomatoes remains unclear. They could have been grown domestically or imported from other countries. Research suggests that the texture of tomatoes makes them more susceptible to bacterial contamination. Since they are often consumed raw, the risk of infection increases as cooking—which would kill harmful bacteria—is not always practiced.
Contaminated water used during cultivation can also contribute to the spread of salmonella. The bacteria can persist in soil and potentially contaminate the fruit as it grows.
Broader Trends in Salmonella Cases
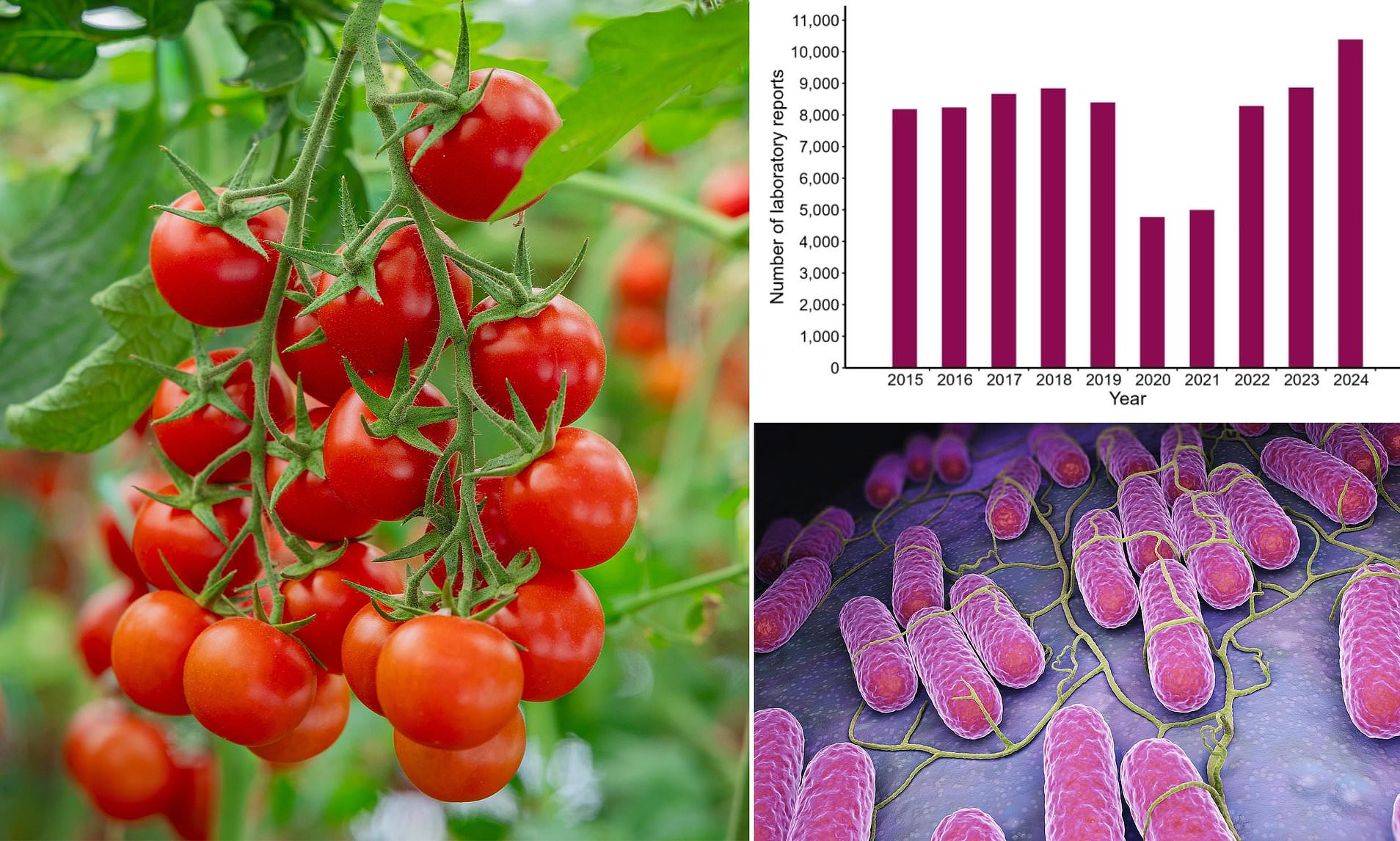
The situation has worsened in 2025, with the UKHSA reporting an even higher number of cases in the first quarter of the year compared to 2024. Between January and March 2025, 1,588 cases were recorded, surpassing the 1,541 cases reported during the same period in 2024. This marks a significant increase from the 1,328 cases logged in the same timeframe in 2023.
These rising numbers have prompted urgent action from health authorities. Dr. James Cooper, deputy director of food policy at the Food Standards Agency (FSA), emphasized the need to investigate the reasons behind the surge in salmonella cases and other pathogens. He stated that this analysis will help implement necessary measures to safeguard public health.
Collaboration and Prevention Efforts
Health officials are working closely with industry stakeholders and local authorities to ensure that food safety standards are met. Businesses are being encouraged to comply with legal requirements to prevent contamination and protect consumers.
Despite these efforts, the persistent rise in salmonella cases highlights the ongoing challenges in maintaining food safety. As the UK continues to monitor the situation, further research and preventive strategies will be essential to curb future outbreaks.
The increasing prevalence of salmonella, especially from uncommon strains, underscores the importance of vigilance in both food production and consumption practices. Public awareness and adherence to hygiene guidelines remain critical in reducing the risk of infection.


Posting Komentar